It’s not always easy to tell if someone has a substance use disorder, especially because of shame and stigma. Some people try to keep their drug use a secret. However, if you suspect someone you love is suffering from addiction, you are not alone. According to the National Institute of Drug Abuse, an estimated 22.7 million Americans, or 8.6% of the population needed drug abuse or alcohol abuse treatment in 2013. Only 2.5 million Americans or 0.9% of the population received treatment at a rehab facility. The significant treatment gap itself speaks for how easy it is to force someone to go to a drug treatment program.
Drug addiction, also called substance use disorder, is a disease that affects a person’s brain and behavior and leads to an inability to control the use of a legal or illegal drug or medication. The risk of addiction and how fast you become addicted varies by drug. Some drugs, such as opioid painkillers, have a higher risk and cause addiction more quickly than others.
If your loved one is showing these outward signs of a substance use disorder, chances are they could be treading the path to dependence. If you have questions about addiction and abuse, the best way to get them answered is by contacting a rehabilitation program directly.

Types Of Addiction
According to ASAM, substance use disorder is when a person is unable to consistently abstain from a behavior or substance. This is typically at the cost of their mental and physical health. Addiction, whether physical or behavioral, impacts many parts of a person’s life. Repeated use of substances or repeated behaviors results in physical brain changes, leading to impaired learning, decision-making, memory and judgment. Over time, addiction causes organ damage and increases risk of contracting a communicable disease. Addiction is known to cause depression and/or suicide and affects relationships with family and friends. Legal problems and financial woes are also common issues that result from addiction.
Substance addiction is dependence on any one or more of the following:
- nicotine, or tobacco
- alcohol
- inhalants, often household items like oven cleaners, spray paints, or other aerosol products
- drugs, illicit or non-illicit
- Medication
Both genetic and environmental factors influence decisions and circumstances that lead to addiction. It is a confusing and challenging path to travel, not only for the person suffering but also for their friends and family members. It’s important to know that no addiction, regardless of what it is to, is untreatable. Professionals can effectively treat addictions of all types, both physical and behavioral.
What Are The Signs Of A Substance Use Disorder?
In the early stages, a person might not show telltale signs of a full-blown addiction. A healthy person can usually identify negative behavior and get rid of it. This is not the case with someone with an addiction. Rather than admit the problem exists, they’ll find ways to justify and continue the behavior. This is why it is crucial to get the necessary help early. Some early stages of a substance use disorder include:
- Experimentation
- Family history of addiction
- Being particularly drawn to an activity or substance
- Seeking out situations where the substance or activity is present
- Episodes of binging or loss of control with little to no feelings of remorse after
When it comes to common social behaviors like drinking or smoking, it might be difficult to determine if there’s an addiction problem. What looks like addiction could be an experimental phase or a form of stress management. But a real addiction, if left untreated, can develop into a debilitating habit or increased risk of illness.
Drugs can also change personalities and behaviors, or make people act in ways that they normally don’t. At first, these behaviors may happen infrequently so it may be hard to notice them. Over time though, they may occur more regularly as drug usage increases.
- Spending more time alone
- Changing friends a lot
- Losing interest in favorite hobbies or usual activities
- Not taking care of appearances (not showering, brushing teeth, changing clothes)
- Having mood swings or being more irritable, tired, or sad
- Sleeping for longer or less, or at different hours than normal
Recognizing Unhealthy Drug Or Alcohol Use In Family Members
Sometimes it’s difficult to distinguish normal teenage moodiness or angst from signs of drug use. Possible indications that your teenager or other family member has a substance use disorder issue include:
- Problems at school or work — frequently missing school or work, a sudden disinterest in school activities or work, or a drop in grades or work performance
- Physical health issues — lack of energy and motivation, weight loss or gain, or red eyes
- Neglected appearance — lack of interest in clothing, grooming, or looks
- Changes in behavior — exaggerated efforts to bar family members from entering his or her room or being secretive about where he or she goes with friends; or drastic changes in behavior and in relationships with family and friends
- Money issues — sudden requests for money without a reasonable explanation; or your discovery that money is missing or has been stolen or that items have disappeared from your home, indicating maybe they’re being sold to support drug use
How Do You Convince Someone They Have A Substance Use Disorder Problem?
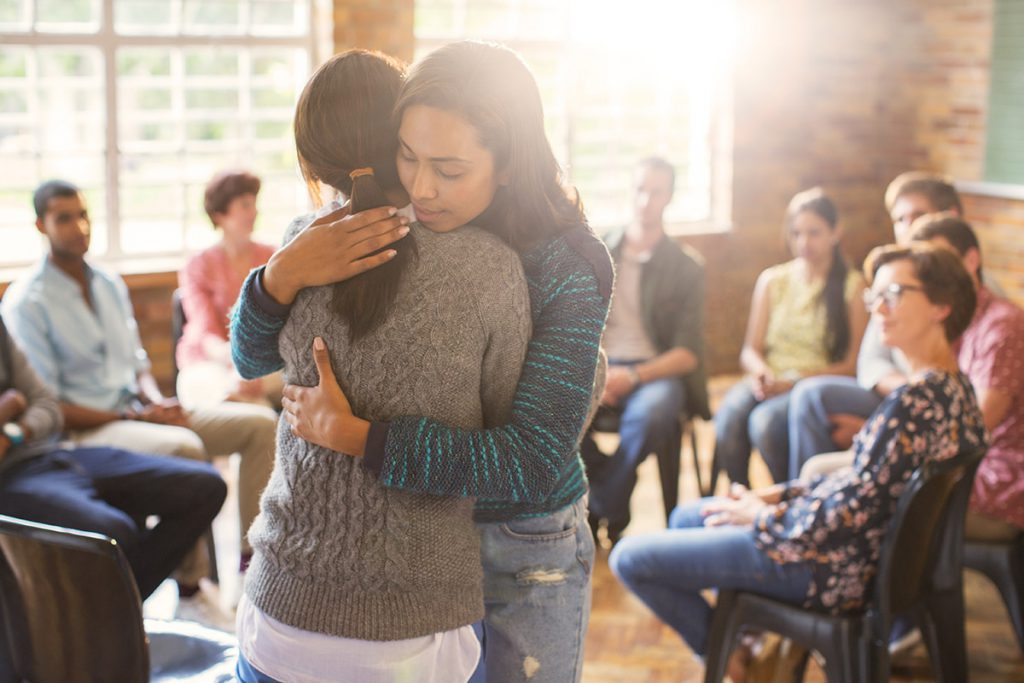
When someone you love habitually misuses alcohol or drugs, it may be clear to you that they need help long before it’s clear to them. A person with substance use disorder is likely to strongly deny that there is a problem. Here are some helpful steps you and your family can take to help a person realize their substance use disorder problem.
- Family intervention. Family members and an interventionist get together with the addict to tell them how they love them and wish that they would get help. Each family member takes a turn and tells the person how special they are and that they need to get help. The person who is struggling listens and perhaps becomes convinced to enter treatment.
- Talk to, not at, the addict. Nobody wants to be lectured. Be honest with the addict and tell him or her that it will require some hard work but that he or she can get better. He or she will suffer without getting help. The person who is struggling is scared and they need help in overcoming their fears and resistance to getting help. Remember to find out those fears, address possible solutions to those fears, and you will have a better chance of getting through to that person.
- Discuss consequences. An addiction expert can have a one-on-one talk with the addict. The expert should warn the addict of the dire consequences if they do not change their ways. The expert should be vivid as possible and hold nothing back. The goal is to convince the person to get help.
- Have someone who’s been there talk to the addict. People who have themselves experienced addiction can try to reason with the addict.
- Ask the addict why he or she won’t get help. Ask the addict to list three reasons why he or she will not get help. At first, he or she will say all kinds of things, but continue to engage the person and get the three main reasons why he or she refuses to get help. It might take a couple of tries, but listen to what he or she says. Once you get the answers, write them down.
- Determine solutions to barriers. Once you get those three reasons, ask a professional to find the solutions to those issues. For example, the person says that he or she will not get help because he or she has failed repeatedly and fears failing again. Ask a few addiction professionals to help the addict overcome this barrier.
- Use your list from no. 3 and list every positive thing that will counter those barriers. When you are finished, present this to the person who is struggling and explain what you came up with. This will help reduce the person’s fears and anxieties and may convince them to get help. Developing a plan to counter their reasons for not getting help will go a long way.
What To Do Next? We Are Here To Help.
For anyone who has a few or all of the signs of a substance use disorder, finding quality drug and alcohol addiction treatment is an important first step. Beginning with a detox period, treatment usually progresses to either an inpatient or outpatient program and is followed by comprehensive aftercare. When a new patient walks through our doors, it’s our priority to make him/her feel comfortable. For us, treating and conquering addiction is personal.